If you find this useful, please leave a comment at the end of the page.
Link to Section A.
Link to Section B. Questions 20 to 23.
Section B
16
This question is about hydrocarbons
(a)
The boiling points of some hydrocarbons containing 6 carbon atoms are shown below.
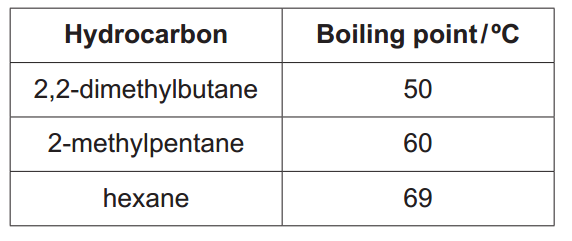
State and explain the trend in boiling points shown by these hydrocarbons.
Trend:
The boiling point increases as the hydrocarbons become less branched (or have fewer methyl/alkyl side groups). Hexane has the highest boiling point, while 2,2-dimethylbutane has the lowest.
Explanation:
All three hydrocarbons are isomers with the same number of electrons. The only intermolecular forces present are London dispersion forces.
- Surface Contact: Less branched molecules, like hexane, have a larger surface area, allowing for greater surface contact between molecules. More branched molecules, like 2,2-dimethylbutane, are more compact, reducing this surface contact.
- Strength of Forces: Greater surface contact leads to more frequent and stronger London dispersion forces between molecules.
- Energy to Boil: More energy is then required to overcome these stronger London dispersion forces, resulting in a higher boiling point for the less branched hydrocarbons.
[4]
(b)
2-methylpentane reacts with bromine by radical substitution.
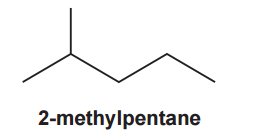
A mixture of organic products is formed, including 3-bromo-2-methylpentane, and compounds A and B.
(i)
Complete the table below to show the mechanism for the formation of 3-bromo-2-methylpentane and three possible equations for termination.
In your equations, use structural or skeletal formulae and ‘dots’ (•) for the position of radicals.
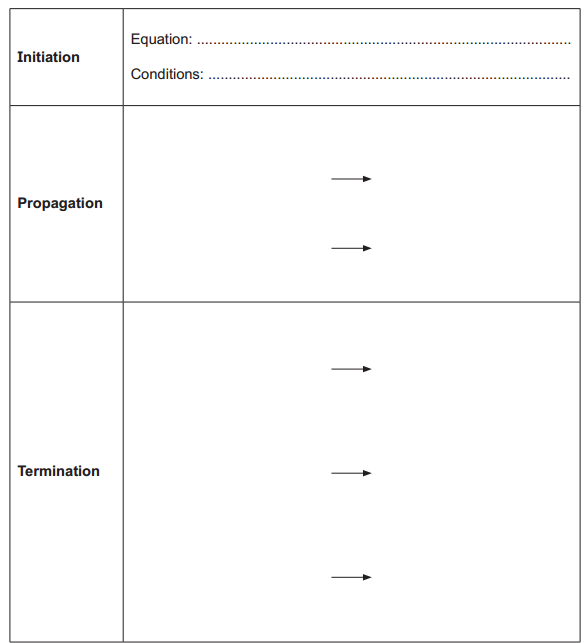
The initiation starts with the formation of free radicals of Bromine with UV light:
Equation: Br2 → 2Br•
Conditions: UV light.
In the propagation, we need to ensure that after each reaction, we have radicals to continue the reaction:
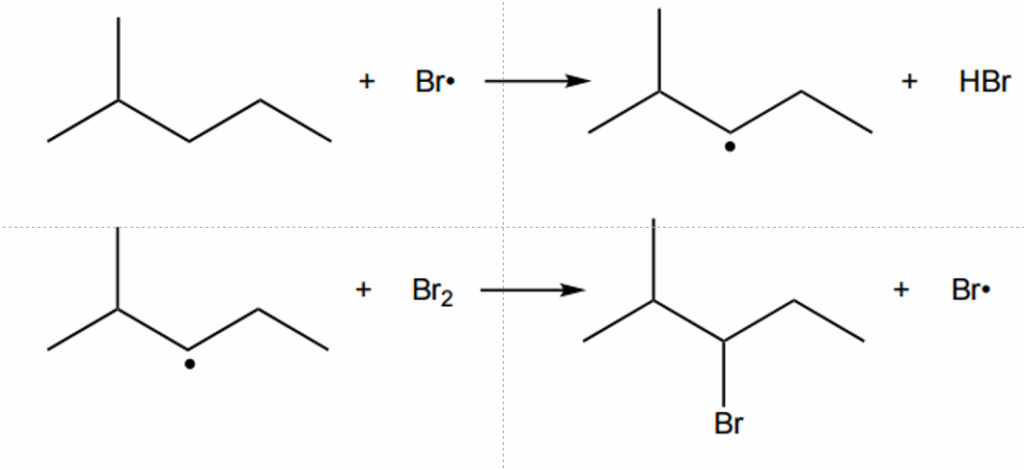
In the termination, we need to ensure that there are no radicals in the products:
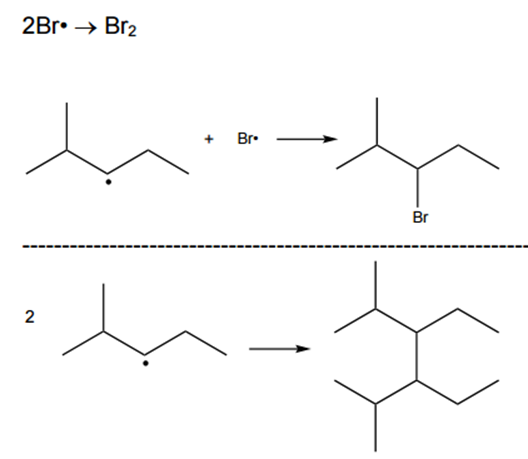
[6]
(ii)
Organic compound A is formed by the substitution of all 14 H atoms in 2-methylpentane by Br atoms.
Write the equation, using molecular formulae, for the formation of compound A from 2-methylpentane.
The reaction is straightforward, just bear in mind that the reaction produces HBr and not H2:
C6H14 + 14 Br2 → C6Br14 + 14 HBr
[2]
(iii)
Organic compound B is formed by the substitution of some of the 14 H atoms in 2-methylpentane by Br atoms.
0.8649g of compound B is heated until it is vaporised.
Under the conditions used:
- compound B has a volume of 72.0 cm3
- the molar gas volume is 40.0 dm3mol–1.
Determine a possible molecular formula of compound B.
With the volume and the molar gas volume, we can find that the number of moles of compound B is:
$$ \small \mathrm{ 72 \, \text{cm}^3 \times \frac{1 \, \text{mol}}{40 \, \text{dm}^3} \times \left(\frac{1 \, \text{dm}}{10 \, \text{cm}}\right)^3 = 1.8 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{mol} } $$
As its mass is 0.8649 g, we can fin that the molar mass is:
0.8649 g / 1.8×10-3 mol = 480.5 g/mol
As the formula of compound B is C6H14-xBrx we can figure out the number of atoms of bromine:
6×12 + (14-x)×1 + 79.9x = 480.5
72 + 14 – x + 79.9x = 480.5
x = (480.5 – 72 – 14) / 78.9 = 5
Therefore, compound B is: C6H9Br5
molecular formula = …….C6H9Br5………….
[3]
17
This question is about alcohols.
(a)
An unsaturated alcohol has 6 carbon atoms and contains one C=C bond.
Construct an equation for the complete combustion of this alcohol.
An easy way to figure out the formula for this alcohol is to sketch out an example that fits the description:
- 6 carbon atoms
- One carbon-carbon double bond (C=C)
- One hydroxyl group (-OH)
For instance, consider: CH₃-CH=CH-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂OH. Counting the atoms we get C₆H₁₂O.
Complete combustion means the alcohol reacts with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). If the combustion wasn’t complete, you’d get carbon monoxide (CO) or even just carbon (soot).
The unbalanced equation looks like this:
C₆H₁₂O + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
We balance the equation step by step:
Carbon (C)
There are 6 carbon atoms in C₆H₁₂O, so we need 6 molecules of CO₂ to balance the carbon
C₆H₁₂O + O₂ → 6CO₂ + H₂O
Hydrogen (H)
There are 12 hydrogen atoms in C₆H₁₂O, so we need 6 molecules of H₂O (since each H₂O has 2 hydrogen atoms) to balance the hydrogen:
C₆H₁₂O + O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
Oxygen (O)
Now, let’s count the oxygen atoms on the right side:
- In 6CO₂: 6 × 2 = 12 oxygen atoms
- In 6H₂O: 6 × 1 = 6 oxygen atoms
- Total oxygen on the right = 12 + 6 = 18 oxygen atoms.
On the left side, the alcohol (C₆H₁₂O) already contributes 1 oxygen atom. This means the remaining 17 oxygen atoms must come from O₂. Since O₂ comes in pairs, we need 17/2 molecules of O₂:
C₆H₁₂O + (17/2)O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
To get rid of the fraction, you can multiply the entire equation by 2:
2C₆H₁₂O + 17O₂ → 12CO₂ + 12H₂O
[2]
(b)
Compound C, shown below, is refluxed with excess acidified potassium dichromate(VI) to form a single organic product and one other product.
Complete the equation for this reaction.
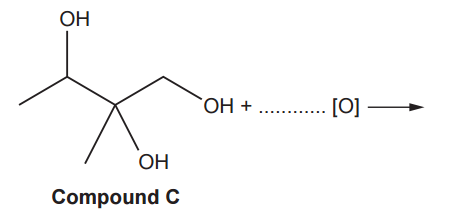
In this reaction, we examine the oxidation under reflux of an alcohol containing primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol groups. The oxidation behaviour varies depending on the type of alcohol:
- Primary alcohols oxidize to form carboxylic acids, passing through an intermediate aldehyde stage.
- Secondary alcohols oxidize to produce ketones.
- Tertiary alcohols do not undergo oxidation under these conditions.
To help with the exam, you can label the carbons in the structure or write the structural formula (skeletal formulas can be harder to interpret at the beginning). The structural formula is:
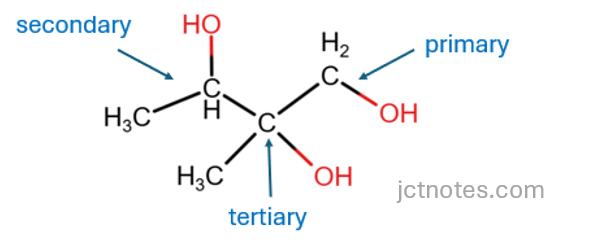
With this information, we can find the single organic product:
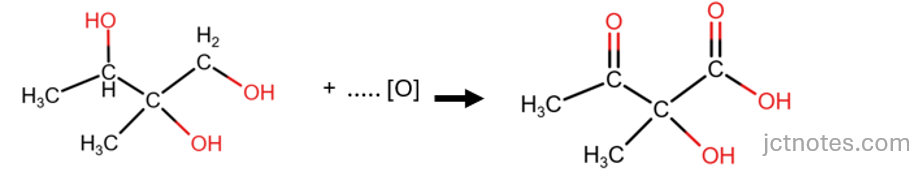
The next step is to balance the reaction. We know that we have one other product, the second product of the oxidation of alcohols under the given conditions is water (H2O). We have lost 4 atoms of H in compound C, then we need 2 molecules of water to account for these H:
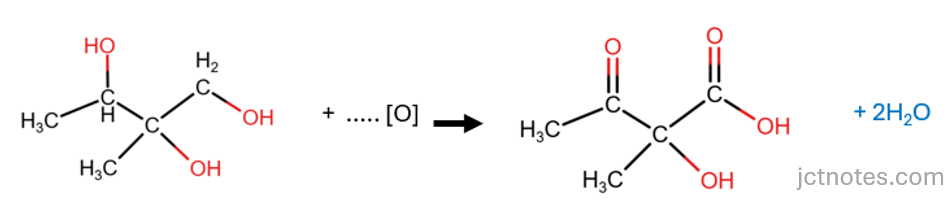
Finally, we balance the oxygen atoms by adding molecules of oxidant:
- In the reactants (left), we have 3 atoms of oxygen from compound C.
- In the products (right):
- we have 4 atoms of oxygen in the organic compound and
- 2 atoms of oxygen given by 2 molecules of water.
- This gives a total of 6 atoms of oxygen.
- To balance the atoms of oxygen, we add 3 molecules of oxidant ([O]):
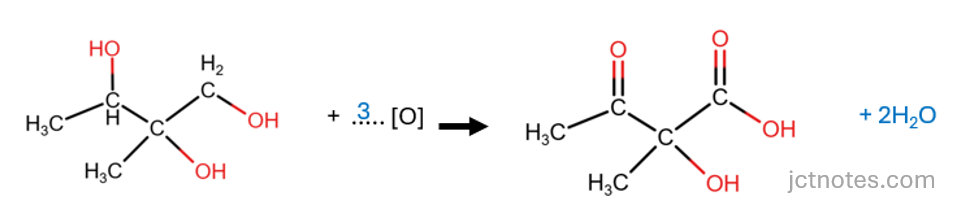
[3]
(c)
Compound D, shown below, is refluxed with H2SO4, as an acid catalyst, to form a mixture of three isomers with the molecular formula C7H10.
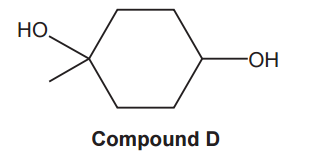
(i)
Draw the structures of the three isomers of C7H10 formed from compound D.
The conditions given produce the dehydration of the alcohol and form double carbon-carbon bonds. Note that there is no oxygen in the product C7H10. I use structural formula to see better what is going on. The product given is:
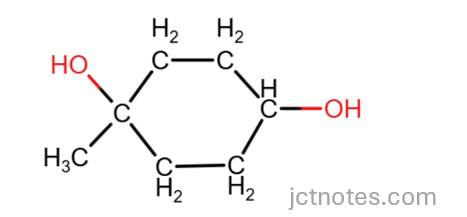
Note that there are not double bonds inside the ring.
We have 2 OH groups, we consider what possibilities we have with each group.
The removal of the OH group on the left can produce a carbon-carbon double bond in 2 positions: outside the ring or inside the ring:
Outside the ring
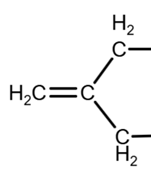
Inside the ring
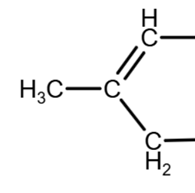
due to geometry, equivalent to
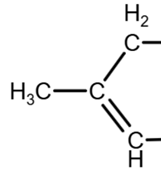
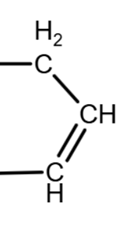
The removal of the OH group on the right can only be done inside the ring (due to the geometry, the double bond can be ‘up’ or ‘down’, as they are equivalent):
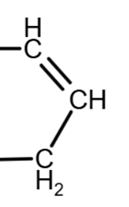
due to geometry, equivalent to
The combination of these location give us the 3 possible isomers:
Isomer 1:
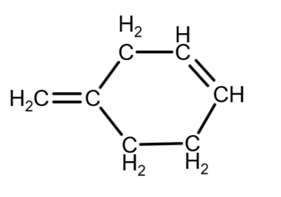
due to the geometry, you can draw it as
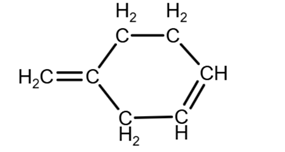
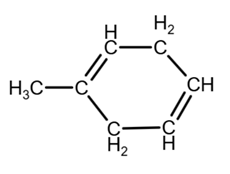
Isomer 2:
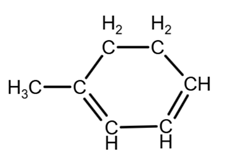
due to the geometry, you can draw it as
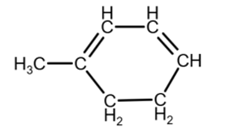
Isomer 3:
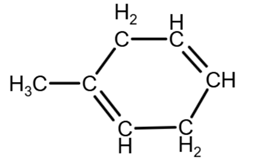
due to the geometry, you can draw it as
[3]
(ii)
A student converts compound D into a diiodoalkane.
Suggest suitable reagents for this reaction.
This is a substitution to form a halogenoalkane, the halogen in this case is iodine. The reagents are NaI (or KI) with H2SO4.
[1]
(d)
There are 4 structural isomers of C4H10O that are alcohols.
A student predicts that these structural isomers could be distinguished using carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy.
Explain whether the student is correct.
In your answer, show how the peaks in the carbon-13 NMR spectra are linked to the structure of each alcohol isomer.
The student is correct because each isomer possesses a unique set of carbon environments, which will result in a different number of signals (peaks) and distinct chemical shifts in their ¹³C NMR spectra. The 4 isomers that we have are:
1. Butan-1-ol presents 4 atoms of C with different environment, giving 4 peaks:
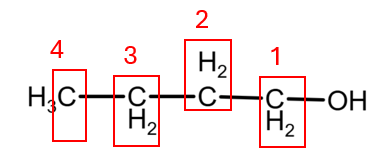
2. Butan-2-ol also presents 4 atoms of C with different environment, giving also 4 peaks:
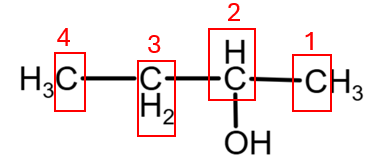
While both butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol would show 4 peaks, the chemical shifts of these peaks would be distinct due to the different environments of each carbon, especially the carbon directly bonded to the hydroxyl group and its neighbours.
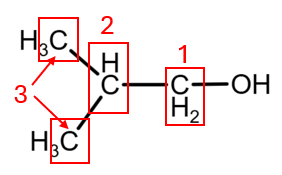
3. 2-Methylpropan-1-ol presents 3 atoms of C with different environment (the CH3 groups give the same peak), giving 3 peaks:
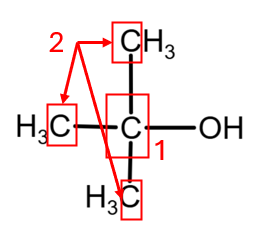
4. 2-Methylpropan-2-ol presents 2 atoms of C with different environment (as the three CH3 groups give the same peak), giving 3 peaks:
[5]
18
1,3-dinitrobenzene is a solid at room temperature.
A chemist prepares 1,3-dinitrobenzene as outlined below.
Step 1
12.5 cm3 of nitrobenzene (density = 1.20 gcm–3) is refluxed with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst.
Step 2
The mixture is cooled. Impure crystals of 1,3-dinitrobenzene appear.
Step 3
The impure crystals are purified to obtain pure 1,3-dinitrobenzenealyst.
The chemist obtains 15.0 g of pure 1,3-dinitrobenzene.
(a)
Outline the mechanism for this reaction, including the role of H2SO4 as a catalyst.
The reaction is an example of an electrophilic substitution.
Step 1: Generation of the nitronium ion (NO₂⁺)
Concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) acts as a catalyst by protonating concentrated nitric acid (HNO₃), leading to the formation of the highly reactive nitronium ion (NO₂⁺), which serves as the electrophile in the reaction. Sulfuric acid is a much stronger acid than nitric acid: the sulfuric acid acts as a proton donor, and nitric acid acts as a base, accepting a proton forming protonated nitric acid (H2NO3+) that is highly unstable and decompose to form nitronium ion and water:
HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ ⇄ H2NO3+ + HSO4– → NO₂⁺ + H2O + HSO4–
Step 2: Attack on nitrobenzene
The nitronium ion then attacks the electron-rich benzene ring in nitrobenzene:
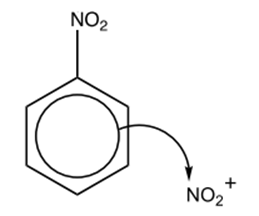
This forms a sigma complex:
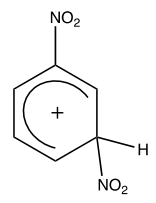
Step 3: Regeneration of aromaticity
The intermediate loses a proton (H⁺), restoring the aromatic structure and yielding 1,3-dinitrobenzene:
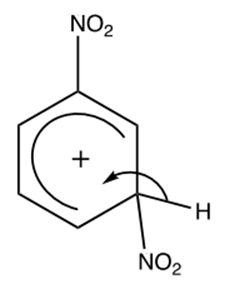
Role of sulfuric acid as catalyst:
The H+ restore the H2SO4, that acts as a catalyst to produce NO₂⁺ and it is reformed at the end of the reaction:
HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ – → NO₂⁺ + H2O + HSO4–
HSO4 – + H+ → H₂SO₄
[5]
(b)
Determine the percentage yield of 1,3-dinitrobenzene.
Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
To determine the amount of 1,3-dinitrobenzene formed assuming complete conversion of nitrobenzene, we can calculate using either the number of moles or masses—both methods yield the same result. Here, I choose to use mass for the calculation.
The molecular masses of nitrobenzene and 1,3-dinitrobenzene are 123 g/mol and 168 g/mol respectively.
With the given density of nitrobenzene (1.20 g/cm3), 12.5 cm3 are:
$$ \small \mathrm{12.5 \, cm^3 \times \frac{1.20 \, g}{1 \, cm^3} = 15 \, g} $$
Since one mole of nitrobenzene yields one mole of 1,3-dinitrobenzene, using the molecular mases, we have that 123 grams of nitrobenzene results in 168 grams of 1,3-dinitrobenzene. Therefore, 15 grams of nitrobenzene will produce:
$$ \small \mathrm{15 \, g \, nitrobenzene \times \frac{168 \, g \, 1,3\text{-}dinitrobenzene}{123 \, g \, nitrobenzene} = 20.487 \, g \, 1,3\text{-}dinitrobenzene} $$
But as we only get 15 grams, the yield, to 3 significant figures is:
$$ \small \mathrm{Yield: \: \frac{15}{20.487} \times 100 = 73.2\%} $$
percentage yield = …………………………………………73.2…. %
[3]
(c)
Describe how to purify the impure crystals in Step 3.
- Dissolution – Dissolve the impure crystals in the minimum volume of hot solvent. Water may be used, but an appropriate organic solvent should be considered depending on solubility.
- Cooling & Crystallisation – Allow the solution to cool to room temperature, promoting the formation of pure crystals. To encourage crystallisation, scratching the inside of the container with a glass rod can help.
- Filtration – Filter the mixture under reduced pressure using a Büchner funnel and flask. This ensures efficient separation of solid crystals from the remaining solution.
- Drying – Leave the filtered crystals to dry in air or in a warm environment, avoiding any drying agents. Drying agents, such as magnesium sulfate or calcium chloride, are commonly used to remove small amounts of water from organic liquids. However, in the case of solid crystals, they are unnecessary and could interfere with purity.
[3]
19
A student intends to synthesise compound Z, as shown in the flowchart below.
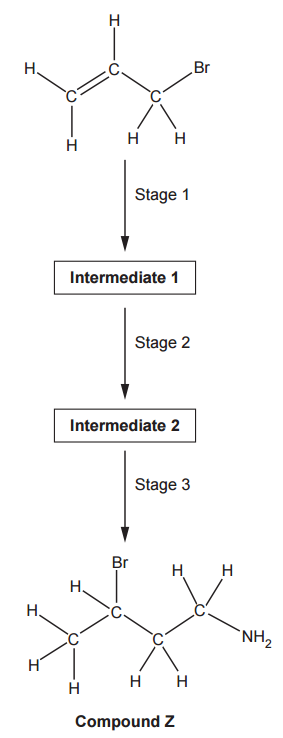
Plan this synthesis showing reagents, the structures of intermediate 1 and intermediate 2, and equations.
To transform the initial compound into compound Z, two key chemical changes occur:
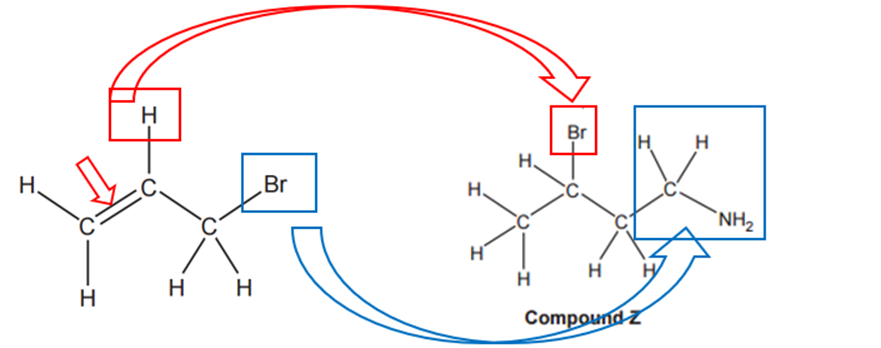
1.
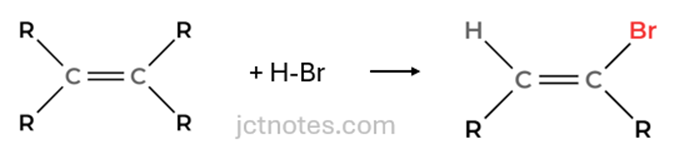
Double Bond to Single Bond with Bromine Addition: The carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) in the initial compound becomes a single bond (C−C), and a bromine atom (Br) is added. This transformation is achieved through a reaction with hydrogen bromide (HBr), which we’ll call Reaction 1.
2.
Bromine to Aminomethyl Group: The bromine atom is replaced by an aminomethyl group (−CH2−NH2). This isn’t a single step; it requires two successive reactions:
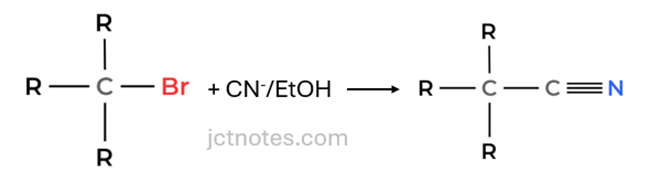
a)
Reaction 2 (Cyanide Addition): The compound’s carbon chain is extended by one carbon, and a nitrogen atom is introduced. This is done by reacting with cyanide ions (CN−) in ethanol, forming a nitrile (−CN) group.
b)
Reaction 3 (Nitrile Reduction): The nitrile group formed in Reaction 2 is then converted into an amine (−NH2) using hydrogen (H2) with nickel (Ni) as catalyst.
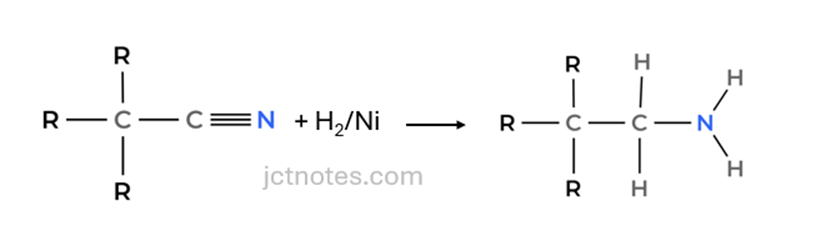
Let’s work through the synthesis in stages:
Stage 1: Introducing the Nitrile Group
We begin by using Reaction 2 to replace the existing bromine with a nitrile group. If we were to use Reaction 1 first, we’d introduce a bromine that would then be removed when Reaction 2 is applied later.
- Reagents: Cyanide (CN−) in ethanol
- Equation: H2C=CHCH2Br + CN− → H2C=CHCH2CN + Br−
- Intermediate 1:
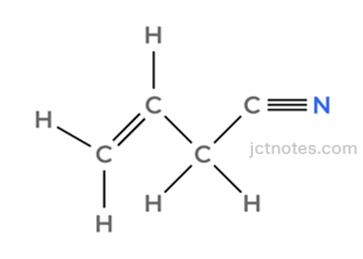
Stage 2: Adding Bromine to the Double Bond
Now, we have two reactions left: Reaction 1 and Reaction 3. If we used Reaction 3 at this point, it would reduce both the nitrile group and the carbon-carbon double bond, preventing us from later inserting the bromine via Reaction 1. Therefore, Reaction 1 must be used next
- Reagents: Hydrogen Bromide (HBr)
- Equation: H2C=CHCH2CN + HBr → CH3CHBrCH2CN
- Intermediate 2:
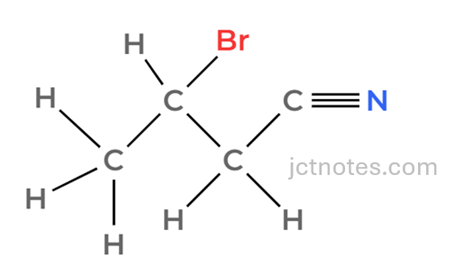
Stage 3: Converting Nitrile to Amine
In the final stage, we use Reaction 3 to convert the nitrile group into an amine.
- Reagents: Hydrogen (H2) with Nickel (Ni) catalyst
- Equation: CH3CHBrCH2CN + 2H2 → CH3CHBrCH2CH2NH2
[6]
Link to Section A.
Link to Section B. Questions 20 to 23.
